EquationFrequencyCovalentBond.jpg
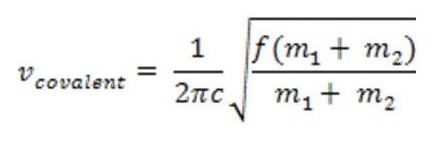
Image courtesy of Kimberly Schipke, M.S.
where f represents the force constant proportional to the strength of the covalent bond and c is the speed of light (2.998e8m/s). The energy/frequency that characterizes the vibration of a particular bond is proportional to the bond dissociation energy. Transitory states between vibrational energies may be induced by absorption or release of infrared radiation. There is a direct correlation between the infrared spectrum and molecular bonding frequencies. In instances of covalent bonds, the greater the change in charge distribution, the stronger the absorption in the infrared spectrum. Also, bonds to hydrogen have higher frequencies due to its lower molecular mass.

